
Financial planning is the task of determining how a business will afford to achieve its strategic goals and objectives. Usually, a company creates a Financial Plan immediately after the vision and objectives have been set. The Financial Plan describes each of the activities, resources, equipment and materials that are needed to achieve these objectives, as well as the time frames involved. A financial plan creates a roadmap for your money and helps you achieve your goals. Financial planning can be done on your own or with a professional.
A financial plan is a comprehensive picture of your current finances, your financial goals and any strategies you’ve set to achieve those goals. Good financial planning should include details about your cash flow, savings, debt, investments, insurance and any other elements of your financial life.
The Financial Planning activity involves the following tasks:
- Assess the business environment
- Confirm the business vision and objectives
- Identify the types of resources needed to achieve these objectives
- Quantify the amount of resource (labor, equipment, materials)
- Calculate the total cost of each type of resource
- Summarize the costs to create a budget
- Identify any risks and issues with the budget set.
Performing Financial Planning is critical to the success of any organization. It provides the Business Plan with rigor, by confirming that the objectives set are achievable from a financial point of view. It also helps the CEO to set financial targets for the organization, and reward staff for meeting objectives within the budget set.
The role of financial planning includes three categories:
- Strategic role of financial management
- Objectives of financial management
- The planning cycle
When drafting a financial plan, the company should establish the planning horizon, which is the time period of the plan, whether it be on a short-term (usually 12 months) or long-term (2–5 years) basis. Also, the individual projects and investment proposals of each operational unit within the company should be totaled and treated as one large project. This process is called aggregation
Having a Financial Plan Matters
The good news is, a 2012 study by the CFP Board (the nonprofit that develops standards for and credentials Certified Financial Planners™) found that “the more extensively households plan, the better prepared they are financially in terms of their likelihood of saving, investing, and managing credit card debt.”
The Board also discovered that 30% of American households are “comprehensive planners,” with strategies for savings and investments, planning for retirement, education, emergencies, major purchases, and insurance needs.
Much of this can be automated, so don’t worry about financial planning becoming a full-time job. Below are five key benefits to having a plan for your finances.
1. A Financial Plan Can Accelerate Savings
While the national savings average is around 5%, the CFP Board found that over half of planners reported saving at least 10% of their income. Planners can then put these dollars to work, with nearly twice as many reporting at least $100,000 in investments than non-planners.
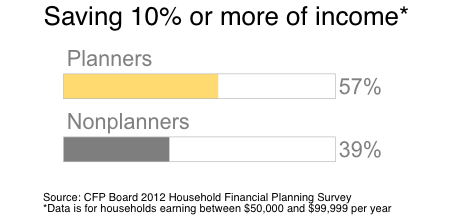
2. A Financial Plan Instills Confidence
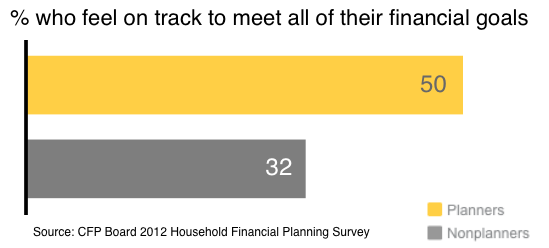
The study found that while only 30% of nonplanners feel very confident about reaching financial goals, 52% of planners can claim this confidence.
That’s because comprehensive planners know exactly where their money is going each month. By taking the mystery out of money, they set themselves up to experience more financial confidence.
3. A Financial Plan Gives Peace of Mind
Imagine the peace of mind that comes with knowing you can cover your monthly expenses, set aside money for long-term goals, and dip into a pile of cash in your wallet for a few guilt-free splurges. Even if that feels out of reach for you now, a plan can propel you in the right direction.
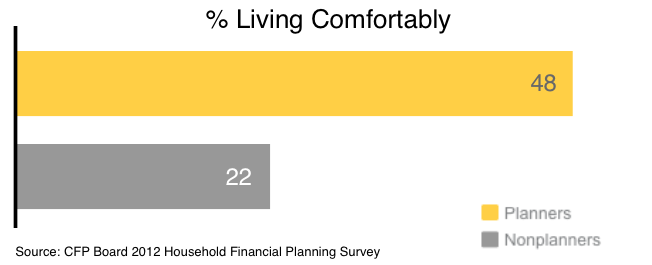
4. A Financial Plan Can Help You Live Comfortably
One key to enjoying life is finding contentment. A personalized financial plan helps you focus on making the most of what you have, rather than bumming out about what you don’t.
Focusing on the options your income creates instead of the limitations of your financial situation could lead to greater contentment. The CFP Board found that 48% of planners described themselves as “living comfortably” — over double the amount of nonplanners.
5. A Financial Plan Can Help You Reach Your Goals
Money has wings. A paycheck hardly settles in an account before it flies away to one obligation or another. Reaching financial goals involves clipping those wings so money sticks around a little longer.
Having a spending, saving, and investing plan in place helps you to keep your hard-earned cash and transforms dreams from nebulous wishes into actionable goals. By gaining a holistic view of your finances, you can get and stay on track toward reaching all of your financial goals.
Sources:
1) The Big Payoff: Educational Attainment and Synthetic Estimates of Work-Life Earnings, U.S. Census Bureau. 2002.
2) Household Financial Planning Survey, CFP™ Board of Standards. 2012.
What is the purpose of the financial planning process?
The purpose of financial planning is to provide you with two things:
- an in-depth analysis of your current financial situation, and…
- a general plan to help you pursue your future goals and objectives.
When we sit down to create your financial plan, our goal is to understand your hopes and dreams for the future, and provide you with a road map to get you from here to there. At Prosperity FInancial Group, we don’t take shortcuts and we aim to provide a holistic approach to the financial planning process.
THE FINANCIAL PLANNING PROCESS
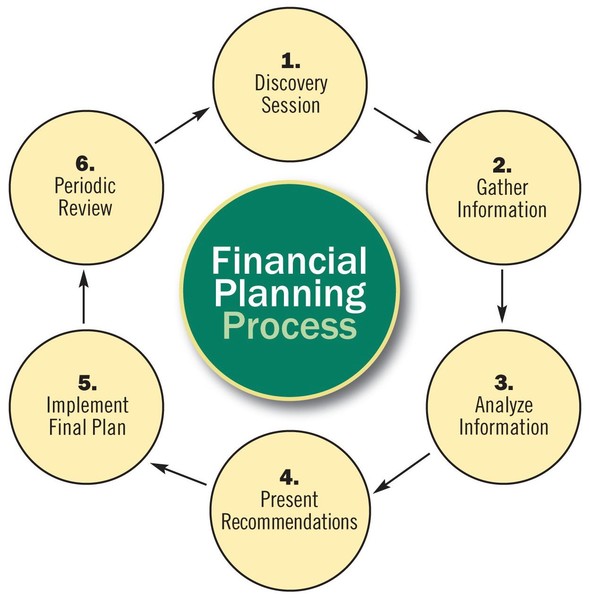
| Most people want to handle their finances so that they get full satisfaction from each available dollar. Typical financial goals include such things as a new car, a larger home, advanced career training, extended travel, and self-sufficiency during working and retirement years. To achieve these and other goals, people need to identify and set priorities. Financial and personal satisfaction are the result of an organized process that is commonly referred to as personal money management or personal financial planning.Personal financial planning is the process of managing your money to achieve personal economic satisfaction. This planning process allows you to control your financial situation. Every person, family, or household has a unique financial position, and any financial activity therefore must also be carefully planned to meet specific needs and goals. A comprehensive financial plan can enhance the quality of your life and increase your satisfaction by reducing uncertainty about your future needs and resources. The specific advantages of personal financial planning include Increased effectiveness in obtaining, using, and protecting your financial resources throughout your lifetime. Increased control of your financial affairs by avoiding excessive debt, bankruptcy, and dependence on others for economic security. Improved personal relationships resulting from well-planned and effectively communicated financial decisions.A sense of freedom from financial worries obtained by looking to the future, anticipating expenses, and achieving your personal economic goals. We all make hundreds of decisions each day. Most of these decisions are quite simple and have few consequences. Some are complex and have long-term effects on our personal and financial situations. The financial planning process is a logical, six-step procedure: (1) determining your current financial situation(2) developing financial goals(3) identifying alternative courses of action(4) evaluating alternatives(5) creating and implementing a financial action plan, and(6) reevaluating and revising the plan. Step 1: Determine Your Current Financial Situation In this first step of the financial planning process, you will determine your current financial situation with regard to income, savings, living expenses, and debts. Preparing a list of current asset and debt balances and amounts spent for various items gives you a foundation for financial planning activities. Step 2: Develop Financial Goals You should periodically analyze your financial values and goals. This involves identifying how you feel about money and why you feel that way. The purpose of this analysis is to differentiate your needs from your wants.Specific financial goals are vital to financial planning. Others can suggest financial goals for you; however, you must decide which goals to pursue. Your financial goals can range from spending all of your current income to developing an extensive savings and investment program for your future financial security. Step 3: Identify Alternative Courses of Action Developing alternatives is crucial for making good decisions. Although many factors will influence the available alternatives, possible courses of action usually fall into these categories: Continue the same course of action.Expand the current situation.Change the current situation.Take a new course of action.Not all of these categories will apply to every decision situation; however, they do represent possible courses of action.Creativity in decision making is vital to effective choices. Considering all of the possible alternatives will help you make more effective and satisfying decisions. Step 4: Evaluate Alternatives You need to evaluate possible courses of action, taking into consideration your life situation, personal values, and current economic conditions. Consequences of Choices. Every decision closes off alternatives. For example, a decision to invest in stock may mean you cannot take a vacation. A decision to go to school full time may mean you cannot work full time. Opportunity cost is what you give up by making a choice. This cost, commonly referred to as the trade-off of a decision, cannot always be measured in dollars. Decision making will be an ongoing part of your personal and financial situation. Thus, you will need to consider the lost opportunities that will result from your decisions. Evaluating Risk Uncertainty is a part of every decision. Selecting a college major and choosing a career field involve risk. What if you don’t like working in this field or cannot obtain employment in it? Other decisions involve a very low degree of risk, such as putting money in a savings account or purchasing items that cost only a few dollars. Your chances of losing something of great value are low in these situations. In many financial decisions, identifying and evaluating risk is difficult. The best way to consider risk is to gather information based on your experience and the experiences of others and to use financial planning information sources.Financial Planning Information Sources Relevant information is required at each stage of the decision-making process. Changing personal, social, and economic conditions will require that you continually supplement and update your knowledge. Step 5: Create and Implement a Financial Action Plan In this step of the financial planning process, you develop an action plan. This requires choosing ways to achieve your goals. As you achieve your immediate or short-term goals, the goals next in priority will come into focus.To implement your financial action plan, you may need assistance from others. For example, you may use the services of an insurance agent to purchase property insurance or the services of an investment broker to purchase stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. Step 6: Reevaluate and Revise Your Plan Financial planning is a dynamic process that does not end when you take a particular action. You need to regularly assess your financial decisions. Changing personal, social, and economic factors may require more frequent assessments.When life events affect your financial needs, this financial planning process will provide a vehicle for adapting to those changes. Regularly reviewing this decision-making process will help you make priority adjustments that will bring your financial goals and activities in line with your current life situation. |

